
This is the principle of compound motion established by Galileo in 1638, and used by him to prove the parabolic form of projectile motion. In projectile motion, the horizontal motion and the vertical motion are independent of each other that is, neither motion affects the other.

5 Projectile motion on a planetary scale.3.2 Trajectory of a projectile with Newton drag.3.1 Trajectory of a projectile with Stokes drag.3 Trajectory of a projectile with air resistance.2.9 Total Path Length of the Trajectory.2.8 Angle θ required to hit coordinate (x, y).2.6 Application of the work energy theorem.2.4 Relation between horizontal range and maximum height.2.2 Time of flight to the target's position.2.1 Time of flight or total time of the whole journey.A ballistic missile is a missile only guided during the relatively brief initial powered phase of flight, and whose remaining course is governed by the laws of classical mechanics.īallistics (from Ancient Greek βάλλειν bállein 'to throw') is the science of dynamics that deals with the flight, behavior and effects of projectiles, especially bullets, unguided bombs, rockets, or the like the science or art of designing and accelerating projectiles so as to achieve a desired performance. Taking other forces into account, such as aerodynamic drag or internal propulsion (such as in a rocket), requires additional analysis. Because of the object's inertia, no external force is needed to maintain the horizontal velocity component of the object's motion. The only force of mathematical significance that is actively exerted on the object is gravity, which acts downward, thus imparting to the object a downward acceleration towards the Earth’s center of mass.
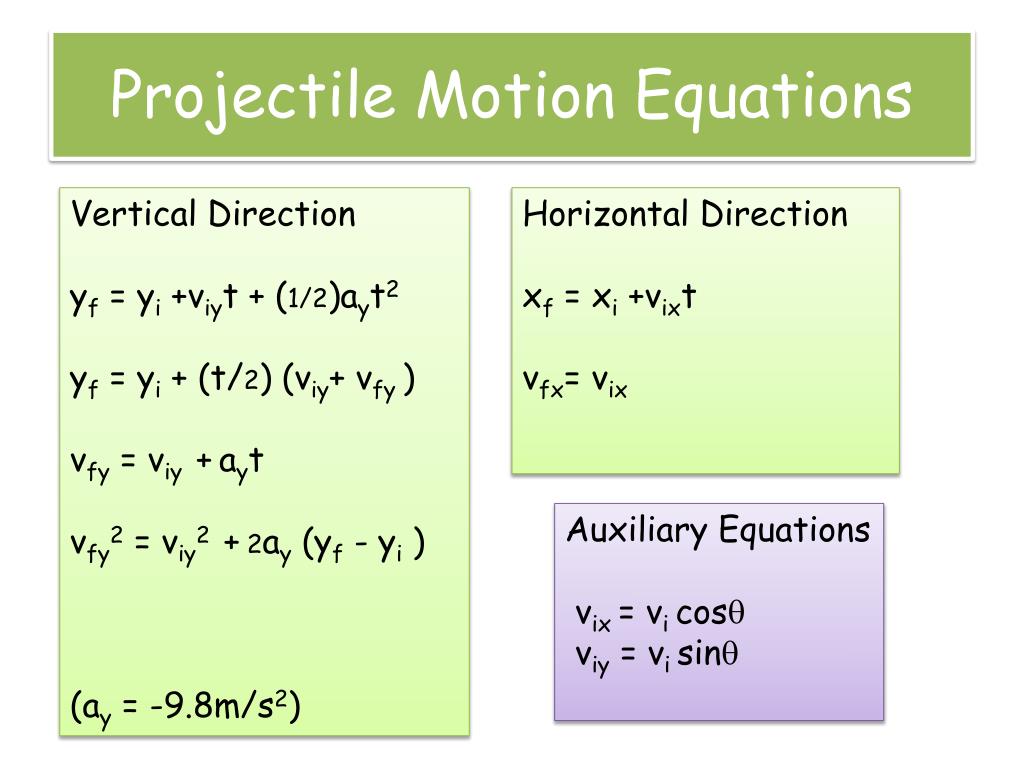
The study of such motions is called ballistics, and such a trajectory is a ballistic trajectory. This curved path was shown by Galileo to be a parabola, but may also be a straight line in the special case when it is thrown directly upwards.

Projectile motion is a form of motion experienced by an object or particle (a projectile) that is projected near Earth's surface and moves along a curved path under the action of gravity only (in particular, the effects of air resistance are passive and assumed to be negligible). Components of initial velocity of parabolic throwing


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
